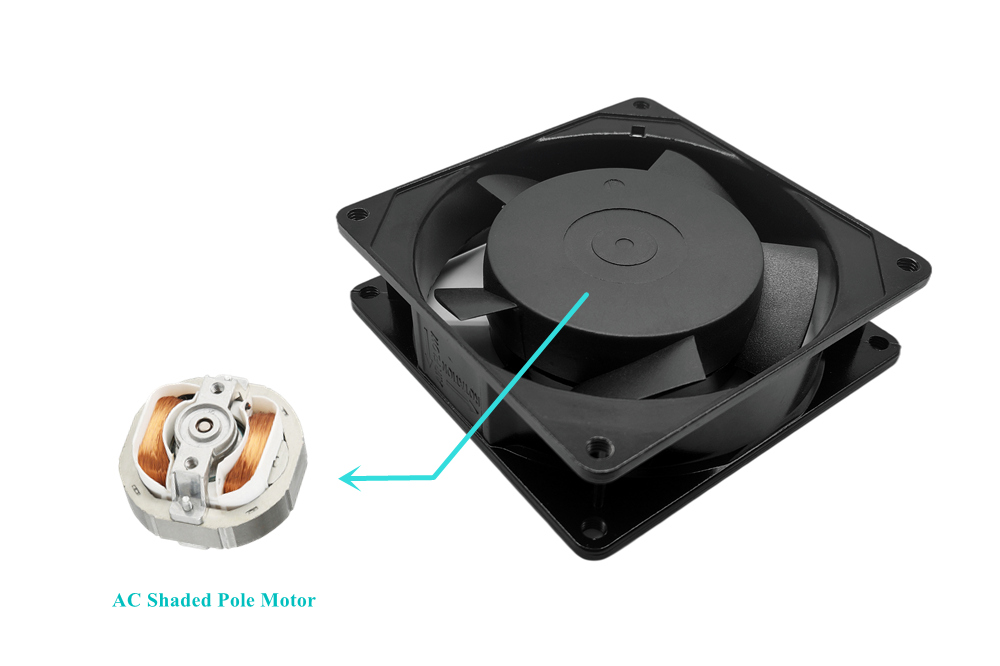
Cooling Fan - AC Shaded Pole Induction Motor
In addition to the DC brushless motor, there is another type of shaded pole induction motor in the exhaust cooling fan.
As the name suggests, Induction motors is because electromagnets in the stator induce magnetism in the rotor. They induce magnetism in the rotor because, unlike the rotor in a brushless DC motor, the rotor in an induction motor contains no magnets.
A separate small winding is used in the stator, called the shielded coil. The electromagnets in the stator are formed by coils around steel laminations. The shading coil is wound around a small section of the laminations. When ac is supplied to the main winding, a portion of the resulting magnetic flux links to the shading coil. This induces a current in the shading coil which behaves like the secondary of a transformer. The induced current, in turn, produces its own (weak) magnetic flux which lags the magnetic flux in the main portion of the stator. Consequently, there is a time and space displacement between the two fluxes. This time and space displacement sets up the conditions for a rotating (or shifting) magnetic field. The rotating magnetic field is what starts and keeps the rotor turning.
Some shielded pole motors do not use shielded coils. Instead, they use a small gap in the lamination, which is enough to generate the hysteresis magnetic field needed to rotate the rotor.
The advantage of AC cooling fan shaded pole motors is that they are inexpensive because they have a pretty simple construction. But the problem is that they are inefficient, mainly because of the lossy linkage between the shaded coil and main winding. The efficiency of shaded pole motors generally is only between 15 and 30%. And the power factor is rather low as well.
A low power factor and efficiency is probably ok for applications where there is only one small cooling fan (shaded pole motors are generally 40 W or less). But consider an application like a data center, which includes racks and racks and racks and racks of severs, and each of those servers has its own fan. It is not advisable to have hundreds or even thousands of fans all operating at only 30% efficiency. Brushless motor technology and its efficiency of 90% are more suitable for these applications.